CROUZON SYNDROME : causes , symptoms , treatments
CROUZON SYNDROME
Crouzon syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorders known as a branchial arch syndrome . specifically , this syndrome affects the first branchial arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible .
This syndrome is named after Octave Crouzon , a French physician who first described this disorder . first called " craniofacial dysostosis " this disorder was characterized by a number of clinical features which can be described by the rudimentary meanings of its former name . Fusion of different sutures leads to abnormal patterns of growth of the skull .
SYMPTOMS OF CROUZON SYNDROME
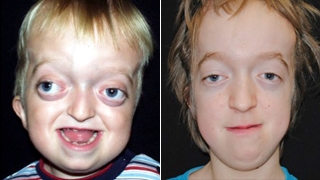
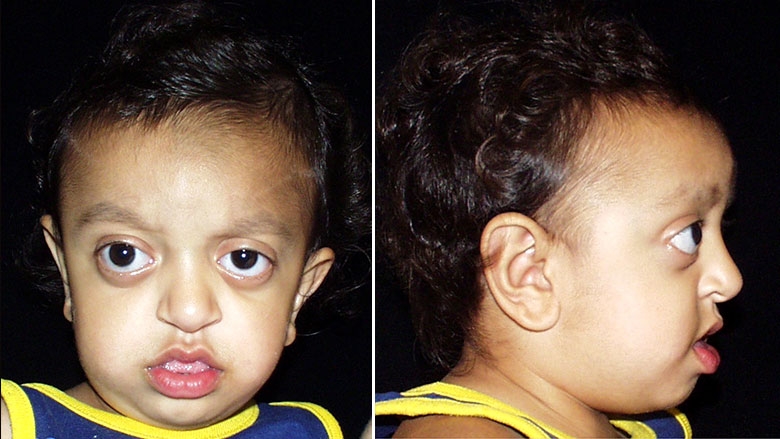
A defining characterized of Crouzon syndrome is craniosynostosis , which results in an abnormal head shape . this is present in combination of frontal bossing , trigonocephaly , brachycephaly , dolichocephaly , premature closure of lambdoid and coronal sutures and complex craniosynostosis .
Other facial characteristics that are present in many cases include external strabismus and hypoplastic maxilla , which results in relative mandibular prognathism and gives the effect of the patient having a concave face .
Most symptoms are secondary to the abnormal skull structure . approximately 30% of people with Crouzon syndrome develop hydrocephalus . the abnormalities in the manner in which the eyes fit in the eye socket can cause vision problems , the most common of which is corneal exposure that can lead to visual impairment . some people with the condition have a restricted airway and can experience severe problem breathing .
CAUSES OF CROUZON SYNDROME
The current research indicates fibroblast growth factor receptors FGFR2 and FGFR3 as the leading factors in causing the autosomal dominant Crouzon syndrome . these two transmembrane proteins are 2 of 4 fibroblast growth factor receptors involved in during embryonic development mutation amongst these receptors are involved in several genetic disorders .
However , the mutation constitutively activates the transmembrane protein via a bond formed incorrectly due to the loss of cysteine 342 . A point mutation causes constitutive activation of tyrosine in the activation loop, located in the cytosolic region of the protein , leading to accelerated differentiation of frontal osteoblasts , resulting in premature fusion of frontal cranial bones .
TREATMENT OF CROUZON SYNDROME
Surgery is typically used to prevent the closure of sutures of the skull from damaging the brain development . to move the orbits forward , surgeons expose the skull and orbits and reshape the bone . to treat the midface deficiency , surgeons can move the lower orbit and midface bones forward .
People with Crouzon syndrome tend to have multiple sutures involved , most specifically bilateral coronal and either open vault surgery or strip craniectomy can be performed . in th latter scenario , a helmet is worn for several months following surgery .
once treated for the cranial vault abnormalities , Crouzon patients generally go on to live a normal lifespan .
Comments
Post a Comment