What is alopecia mucinosis & how to treat them ?
WHAT IS ALOPECIA MUCINOSA ?
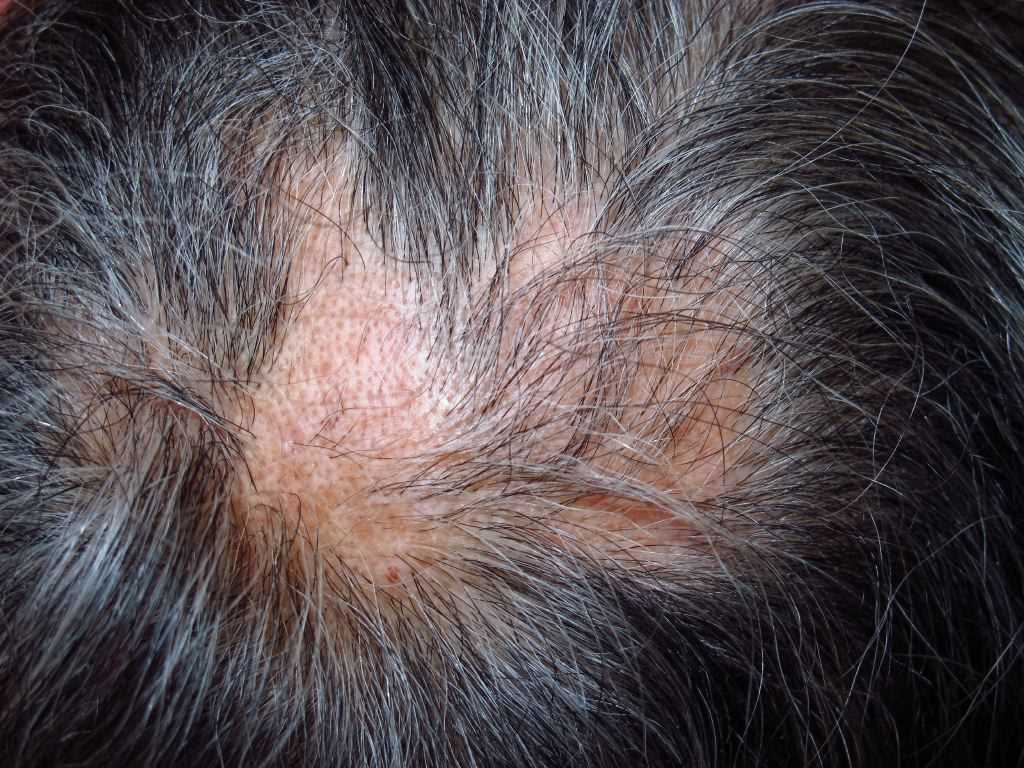
Alopecia mucinosa, also known as follicular mucinosis , describes the appearances of mucin around hair follicles as seen under the microscope . it is characterised by bald patches of skin in which hair follicles are prominent .
Mucin look like stringly clear or whitish goo mainly composed of hyaluronic acid, a normal component of the ground substances surrounding collagen in the dermis. Several other forms of mucinosis are described and classified .
- a primary and acute disorder occuring in children and adolescents .
- a primary and chronic disorder occuring in people older than 40 years .
- a secondary disorder associated with benign or malignant skin disease
- urticaria like follicular mucinosis .
Pictures of Alopecia Mucinosa :
What causes of alopecia mucinosa ?
What are the features of alopecia mucinosa ?
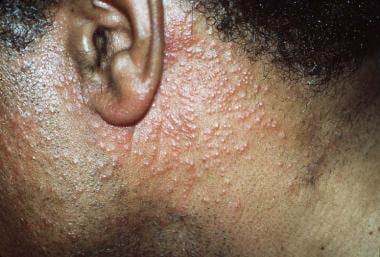
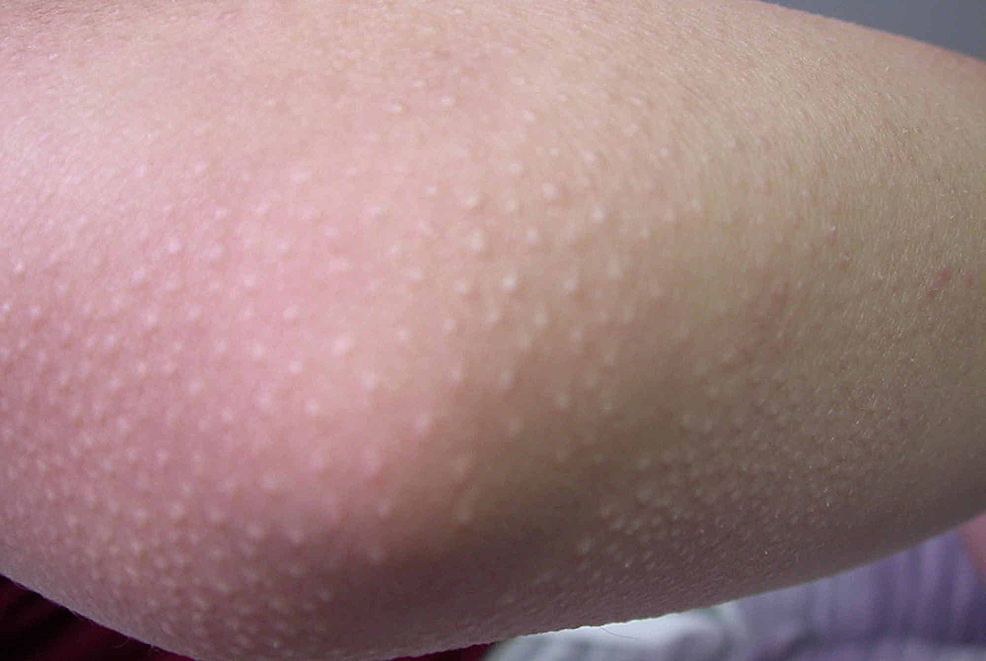
- it presents as grouped follicular papules within reddened , dry , patches or plaques.
- one or more lesions may be present from onset or a single lesion may develop to multiple lesion over a few weeks or months .
- patches or plaques are usually 2-5 cm in diameter but can be larger .
- Hair loss is non scarring and potentially reversible in the early stages , but in more advanced disease the hair follicles are destroyed , causing scarring alopecia .
- Affects people < 40 years .
- Usually , only one or a few lesions arise .
- They are often located on the head , neck and upper arm .
- Most resolve spontaneously within 2 months to 2 years .
- Affects people > 40 years
- Widespread and often numerous lesion may persist or recur indefinitely
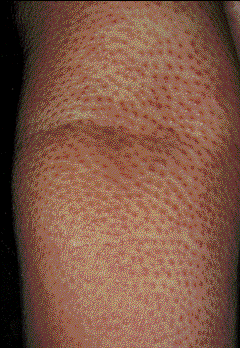
- it presents as flat or raised patches that may rarely ulcerate
- permanently bald patches are studded with horny plugs
- sometimes mucin can be squeezed out of affected follicles
- presents as itchy small bumps or raised areas
- these are mostly found on the head and neck
- Affects people > 40 years
- Follicular mucinous degeneration may arise in inflammatory skin diseases such as lupus erythematosus and lichen simplex .
- It may also arise in malignant disease such as cutaneous T cell lymphoma , kaposi sarcoma and hodgkin lymphoma
- Skin features typical of teh underlying disease may also be present
- A skin biopsy is necessary to distinguish these from primary alopecia mucinosa
What are the treatments for alopecia mucinosa ?
- Topical , intralesional and systemic corticosteroids
- Oral antibiotics such as minocycline
- Dapsone
- Indomethacin
- interferons
- topical and systemic photochemotherapy
- topical nitrogen mustard
- Radiation therapy
- UVA1 phototherapy
- Topical bexarotene 1%gel
Secondary alopecia mucinosa should be treated appropriately for the underlying skin disease , particular if it is cutaneous T cell lymphoma .


Comments
Post a Comment