what is Angular Cheilities ?
Angular Cheilities :
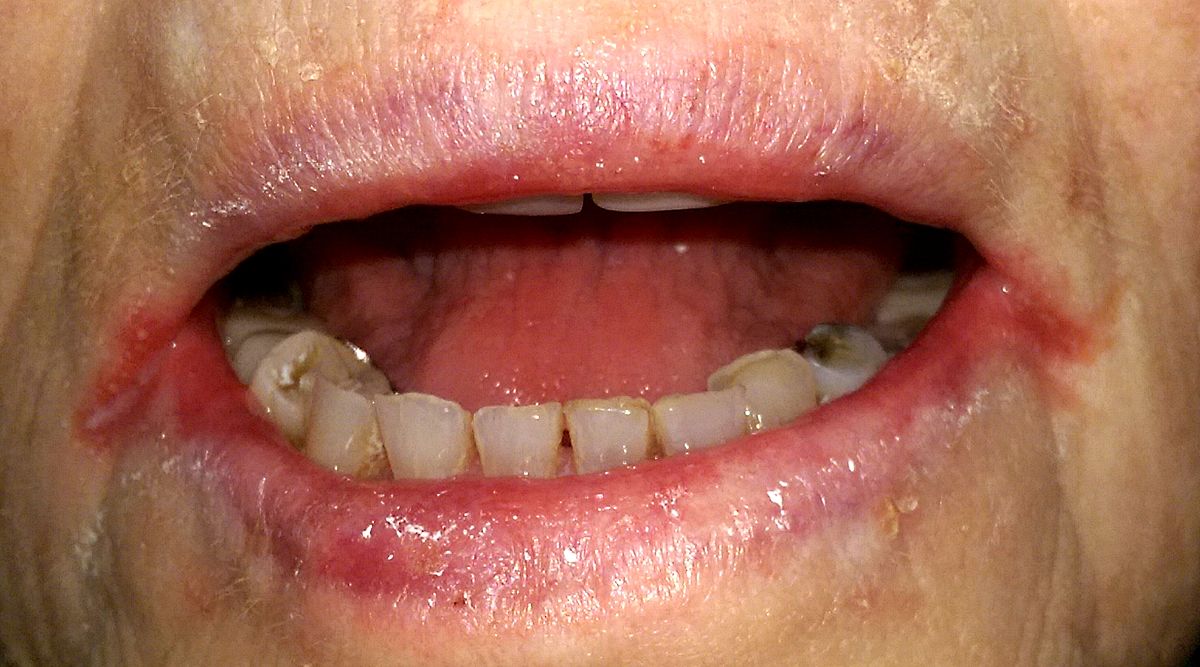
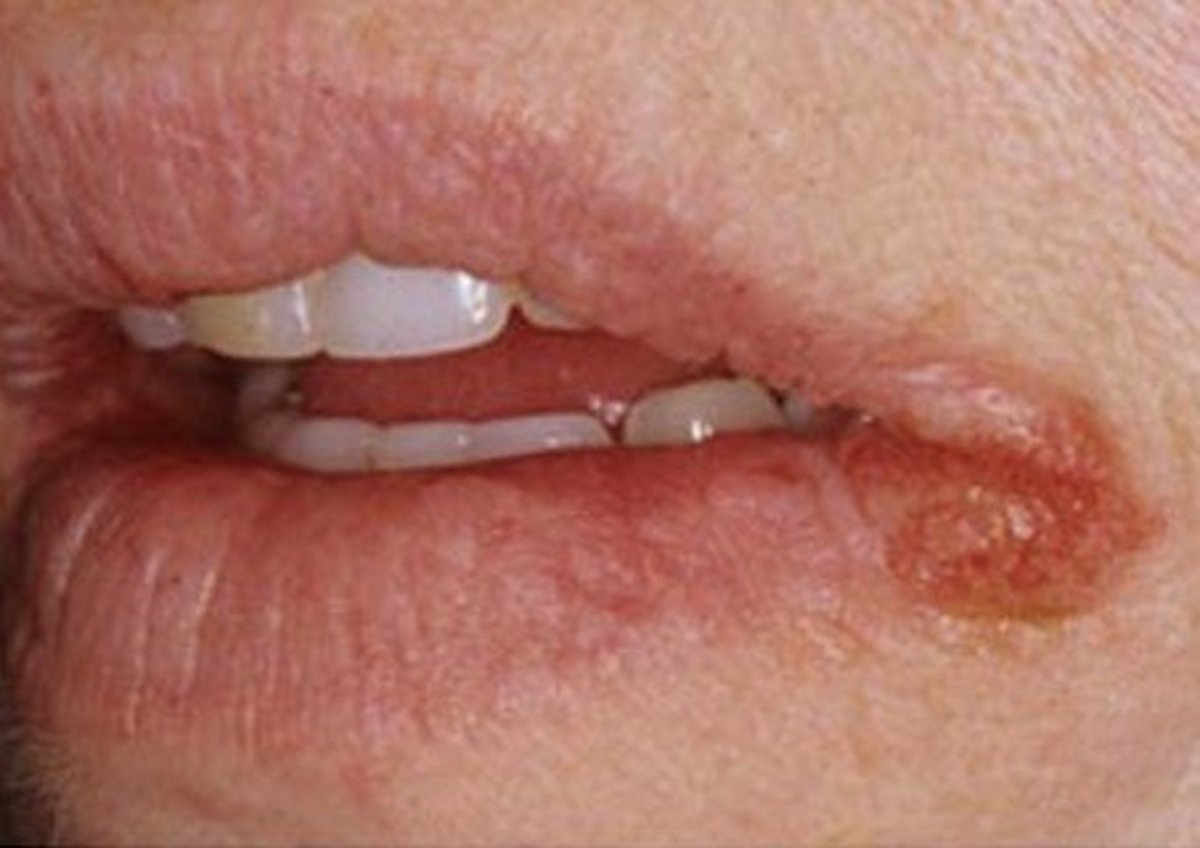
Angular cheilities is a type of mouth sore that appears at the corners of the mouth. Also, known as angular stomatitis and perleche , this condition can cause swollen , red patches in the corners and on the outside of your lips . angular cheilitis is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth . often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting . it can also be itchy or painful . the condition can last for days to years . angular cheilities is a type of cheilities .
Angular cheilitis can be caused by infection , irritation , or allergies . infections include by fungi such as candida albicans and bacteria such as staph aureus . Irritants include poorly fitting dentures , licking the lips or drooling , mouth breathing resulting in a dry mouth , sun exposure , overclosure of the mouth , smoking and minor trauma . Other factors may include poor nutrition or poor immune function . Diagnosis may be helped by testing for infections and patch testing for allergies .
WHAT ARE CAUSES OF ANGULAR CHEILITIES ?
Angular cheilities is thought to be multifactorial disorder of infectious origin , with many local and systemic predisposing factors . the sores in angular cheilities are often infected with fungi bacteria or a combination thereof this may represent a secondary , opportunistic infection by these pathogens . some studies have linked the initial onset of angular cheilitis with nutritional defiencies especially of the B vitamin & iron , which in turn may be evidence of malnutients or malabsorption . Angular cheilities can be a manifestation of contact dermatitis , which is considered in 2 groups - irritational and allergic . A lesion caused by recurrence of a latent herpes simplex infection can occur in the corner of the mouth . Rather than utilizing antifungal creams , angular herpes simplex is treated in the same way as a cold sore , with topical antiviral drugs such as aciclovir .
SIGN & SYMPTOMS OF ANGULAR CHEILITIES :
Angular cheilitis is a fairly non specific term which describe the presences of an inflammatory lesions in a particular anatomic site . as thre are different possible causes and contributing factors from one person to the next , the appearences of the lesion is somewhat variable , the lesions are more commonly symmetrically present on both sides of the mouth , but sides of the mouth but sometimes only one side may be affected . Initially the corners of the mouth develop a gray white thickening and adjacent erytherma . Later the usual appearences is a roughly triangular area of eythema , edema and breakdown of skin at either corner of the mouth . The mucosa of the lip may become fissured crustd, ulcerated or atrophied . There is not usually any bleeding .
Sometimes contributing factors can be readily seen, such as loss of lower face height from poorly made or worm dentures, which results in mandibular overclosure . If there is a nutritional deficiency the condition , various othre signs and symptoms such as glossitis may be present . In people with angular cheilitis who were dentures, often there may be erythematous mucosa underneath the denture , an appearence consistent with denture - related stomatitis . typically the lesions give symptoms of soreness , pain , pruritus or burning or a raw feeling .
DIAGNOSIS OF ANGULAR CHEILITIES :
Angular cheilities is noormally a diagnosis made clinically . the sore is unilateral rather than bilateral , this suggests a local factor or a split syphilitic papule . Angular cheilities caused by mandibular overclosure , drooling and othre irritants is usually bilateral . The lesion are normally swabbed to detect Candida or bacterial species may be present . Persons with angular cheilitis who wear dentures often also will have their dentures swabbed in addition . A complete blood count may be indicated , including assessment of the levels of iron , ferritin , vitamin B12 and folate .
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OF ANGULAR CHEILITIS ?
General Measures :
improved general hydration
use of lip balm or a thick emollient ointment applied frequently often sufficient treatments alone for saliva induced angular cheilitis .
topical antiseptics
Specific Measures :
topical antifungal cream
oral antifungal medication
topical or oral antistaphylococcal antibiotic
topical steriod ointment if the skin is significantly inflamed
HOW TO PREVENT ANGULAR CHEILITIS ?
- education around reduced licking of the lips
- nutritional supplements
- quitting smoking of cigarettes
- use of topical emollients /lip balm to keep lips from being too dry
- rinsing the mouth after use of inhaled corticosteroids
- maintaining good oral and denture hygiene
- Filler injections or implants to build up the oral commissures
- improved blood glucose control in those with diabetes mellitus
- botulinum toxin to smooth out mouth furrows


Comments
Post a Comment