Is follicular tonsilitis infectious ?
TONSILITIS :
Tonsillitis occurs when your tonsils become infected. Tonsils are the two small lumps of soft tissue — one on either side — at the back of your throat. You can see your tonsils in a mirror by opening your mouth and sticking out your tongue.
Part of your immune system tonsils help trap germs that make you sick. When your tonsils become infected, they get swollen and sore, and swallowing may hurt. Tonsillitis is also called tonsillopharyngitis, but most people call it a sore throat .
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF TONSILITIS ?
Tonsillitis symptoms usually come on suddenly. They may include:
- Sore or scratchy throat.
- Pain or difficulty swallowing.
- Red, swollen tonsils and throat.
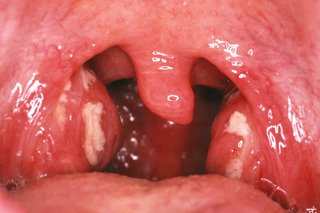
- Whitish spots on your tonsils — or a white, yellow or gray coating on your tonsils.
- Fever above 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius).
- Swollen lymph nodes (glands on the sides of your neck below your ears).
- Stomachache or vomiting (more common in younger children).
Those with tonsillitis usually experience sore throat, painful swallowing, malaise, and fever.Their tonsils – and often the back of the throat – appear and swollen, and sometimes give off a white discharge. Some also have tender swelling of the cervical lymph nodes.
Many viral infections that cause tonsillitis will also cause cough, runny nose, hoarse voice, or blistering in the mouth or throat.Infectious mononucleosis can cause the tonsils to swell with red spots or white discharge that may extend to the tongue. This can be accompanied by fever, sore throat, cervical lymph node swelling, and enlargement of the liver and spleen.Bacterial infections that cause tonsillitis can also cause a distinct "scarletiniform" rash, vomiting, and tonsillar spots or discharge.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF TONSILITIS ?
Tonsillitis can also stem from infection with bacteria, predominantly Group A β-hemolytic streptococci (GABHS), which causes strep throat. Bacterial infection of the tonsils usually follows the initial viral infection. When tonsillitis recurs after antibiotic treatment for streptococcus bacteria, it is usually due to the same bacteria as the first time, which suggests that the antibiotic treatment was not fully effective.
Anaerobic bacteria have been implicated in tonsillitis, and a possible role in the acute inflammatory process is supported by several clinical and scientific observations. Sometimes tonsillitis is caused by an infection of spirochaeta and treponema, which is called Vincent's angina or Plaut-Vincent angina. Within the tonsils, white blood cells of the immune system destroy the viruses or bacteria by producing inflammatory cytokines like phospholipase Awhich also lead to fever. The infection may also be present in the throat and surrounding areas, causing inflammation of the pharynx.
HOW IS TONSILITIS DIAGNOSED ?
In primary care settings, the Centor criteria are used to determine the likelihood of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS) infection in an acute tonsillitis and the need of antibiotics for tonsillitis treatment.However, the Centor criteria have their weaknesses in making precise diagnosis for adults. The Centor criteria are also ineffective in diagnosis for tonsillitis in children and in secondary care settings (hospitals).A modified version of the Centor criteria, which modified the original Centor criteria in 1998, is often used to aid in diagnosis. The original Centor criteria had four major criteria but the modified Centor criteria have five. The five major criteria of the modified Centor score are:
- Presence of tonsillar exudate
- Painful neck lymph nodes
- History of fever
- Age between five and fifteen years
- Absence of cough
The possibility of GABHS infection increases with increasing score. The probability for getting GABHS is 2 to 23% for the score of 1, and 25 to 85% for the score of 4.The diagnosis of GABHS tonsillitis can be confirmed by culture of samples obtained by swabbing the throat and plating them on blood agar medium. This small percentage of false-negative results are part of the characteristics of the tests used but are also possible if the person has received antibiotics prior to testing. Identification requires 24 to 48 hours by culture but rapid screening tests (10–60 minutes), which have a sensitivity of 85–90%, are available. In 40% of the people without any symptoms, the throat culture can be positive. Therefore, throat culture is not routinely used in clinical practice for the detection of GABHS.
Bacterial culture may need to be performed in cases of a negative rapid streptococcal test. An increase in antistreptolysin O (ASO) streptococcal antibody titer following the acute infection can provide retrospective evidence of GABHS infection and is considered definitive proof of GABHS infection, but not necessarily of the tonsils. Epstein Barr virus serology can be tested for those who may have with a typical lymphocyte count in full blood count result. Blood investigations are only required for those with hospital admission requiring intravenous antibiotics.
HOW TO TREAT TONSILITIS INFECTIOUS ?
Antibiotics
If the tonsillitis is caused by group A streptococcus, then antibiotics are useful, with penicillin or being primary choices. are considered good alternatives to penicillin in the acute care setting. A macrolide, such as azithromycin or erythromycin, is used for people allergic to penicillin. If penicillin therapy fails, bacterial tonsillitis may respond to treatment effective against beta-lactamase producing bacteria such as clindamycin or amoxicillin-clavulanate. Aerobic and anaerobic beta lactamase producing bacteria that reside in the tonsillar tissues can "shield" group A streptococcus from penicillins. There is no significant difference in efficacy of various groups of antibiotics for treating tonsillitis. Intravenous antibiotics can be for those who are hospitalized with inability to swallow and presented with complications. Oral antibiotics can be resumed immediately if the person is clinically improved and able to swallow orally. Antibiotic treatment is usually taken for seven to ten days.
Pain medication
Paracetamol and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to treat throat pain in children and adults.Codeine is avoided in children under 12 years of age to treat throat pain or following tonsilectomy. NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen) and opioids (such as codeine and tramadol) are equally effective at relieving pain, however, precautions should be taken with these pain medications. NSAIDs can cause peptic ulcer disease and kidney damage. Opioids can cause respiratory depression in those who are vulnerable. Anaesthetic mouthwash can also be used for symptomatic relief.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids reduce tonsillitis pain and improve symptoms in 24 to 48 hours. Oral corticosteroids are recommended unless the person is unable to swallow medications.
Surgery
When tonsillitis recurs frequently, often arbitrarily defined as at least five episodes of tonsillitis in a year, or when the palatine tonsils become so swollen that swallowing is difficult as well as painful, a tonsillectomy can be performed to surgically remove the tonsils.
Children have had only a modest benefit from tonsillectomy for repeated cases of tonsillitis



Comments
Post a Comment