What is the treatment for toxic epidermal necrolysis?
TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS [ TEN ] :
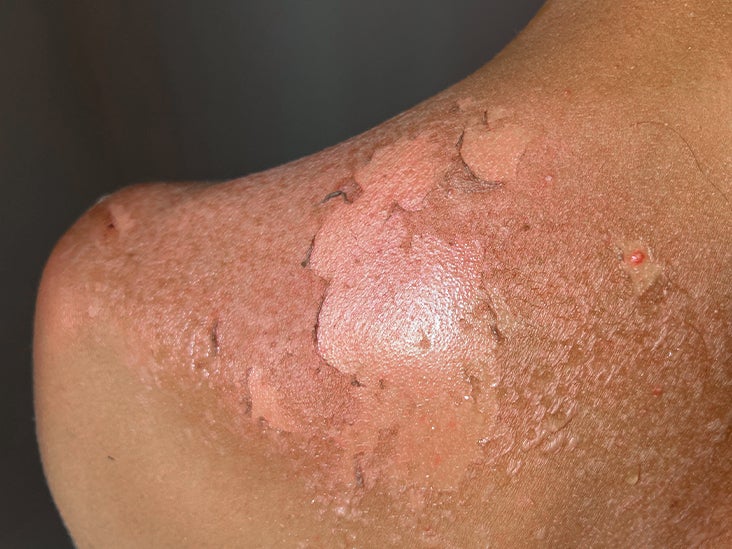
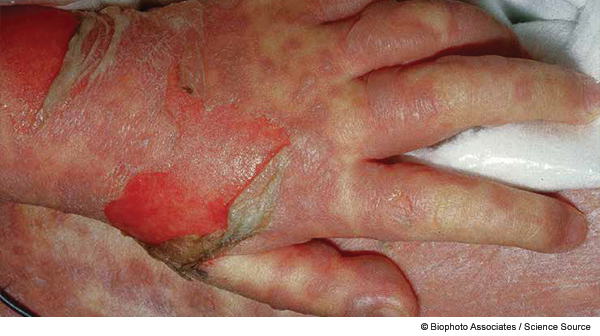
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is a painful, life-threatening skin condition. It causes large areas of blistering and peeling skin on at least 30% of your body, including mucous membranes like the mouth, eyes and genitals. It's the result of a reaction to certain medications. Widespread damage to the skin can lead to dangerous fluid loss and infections.
TEN, or TEN syndrome, is a rare, severe form of Stevens Johnson syndrome (SJS). SJS causes blistering and peeling skin on less than 10% of the body. The two conditions overlap when there is 10% to 30% body coverage. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is a life-threatening skin condition. It causes peeling and blistering skin over much of the body, including the mouth, eyes, and genitals. TEN is the most severe form of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Both conditions are caused by a reaction to medication. About 25% of people who develop TEN don’t survive.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECCROLYSIS?
In most cases, experts think that certain medications trigger TEN syndrome. These medications may include:
- Allopurinol (drug used to treat and gout).
- Anticonvulsants (group of drugs used to treat seizures).
- Anti-retroviral drugs used to treat HIV (especially NNRTIs like nevirapine, efavirenz, or etravirine).
- Oxicams (a group ofnon or NSAIDs).
- Sulfonamides (a type of antibiotic).
Other rare triggers may include:
- Infections
- Vaccinations.
There are some cases where the cause of TEN is not known.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS ?
TEN symptoms may develop a few weeks after you start taking a medication. It usually begins with flu-like symptoms, including:
- Body aches.
- Cough
- Fever and chills.
- Headache
- Redness and inflammation in the eyes.
TEN then causes a painful skin rash before progressing to large areas of blistering and peeling skin. Erosions, or painful open wounds that look like burns, develop as the skin peels away.
Erosions tend to start on the face and chest. They often spread to the following areas of the body:
- Eyes, including the conjunctiva (inside of the eyelid) and cornea (outer lens of the eye).
- Mucous membranes, including inside the mouth, nose, throat and airways.
- Urinary tract, anus and genitals.
Erosions can make it difficult and painful to eat, swallow, breathe, see, urinate and perform other functions.
HOW IS TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS DIAGNOSED ?
Your healthcare provider can usually diagnose TEN after evaluating your skin and symptoms. In some cases, you may need a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. A pathologist (healthcare provider who examines body tissues) studies a sample of your skin under a microscope. The biopsy shows:
- Necrotic (dead) skin cells.
- Detachment of the first layer of skin (epidermis) from the second layer.
TEN requires emergency medical treatment at a hospital. You’ll receive care in an intensive care unit (ICU) or burn center. Immediate treatment includes:
- Stopping all medications that could be triggering TEN.
- Replacing lost body fluids through an IV.
- Preventing skin infections with antibacterial creams or ointments.
- Giving antibiotics at the first sign of infection.
Other treatments for TEN may include:
- Immune globulin: You receive immune globulin through an IV. It’s a sterile liquid made from donor plasma (the liquid part of the blood). It contains antibodies or substances that help your body fight infections.
- Immunosuppressants: These drugs weaken the immune system when it isn’t working right. They keep your body from attacking its own tissues.
- Plasmapheresis: This procedure removes blood from your body and separates the plasma from blood cells. A machine removes substances causing a harmful immune response from the plasma. Then, the machine returns the “clean” blood or a plasma substitute to your body.
Comments
Post a Comment